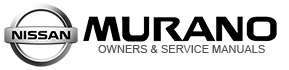Nissan Murano: Safety and Health / Precautions for Operation
In body repair, great importance is attached to quality, efficiency and cost. Consideration for workers' safety and health should, however, be deemed as the most important item. In reality, it is essential that measures be established to prevent accidents and to make the work environment safer and healthier.
-
While working, suitable work clothes, a work cap and safety shoes must be worn. To prevent burns, a long sleeve shirt and trousers must also be worn and must not be taken off under any circumstances.
-
Use welding respirator
-
Keep work clothes clean. Do not keep a lighter or other flammable materials in pockets.
-
During oxygen and acetylene gas welding, to protect eyes wear goggles according to the quantity of infrared rays.
-
During arc welding, to protect eyes wear a safety goggles with a shading plate according to the quantity of ultraviolet rays.
-
Gloves, apron, foot covers, earplugs and arm covers should be used to prevent burns.
The occupational safety regulations include provisions on preventative measures for avoiding damage and accidents. As the occupational safety regulations are country- specific, this document only lists general information on occupational health and safe- ty for working with steel. The general, non-material-specific protection and hygiene measures in the workshop must always be observed.
Protective equipment
The following table provides an overview of the general personal protective equipment for material processing:
| Protective equipment | MAG welding | Spot welding | Sanding / Grinding & Cutting |
| Protective shoes | X | X | X |
| Work clothing | X | X | X |
| Safety goggles | X | X | |
| Welding gloves | X | ||
| General protection gloves | X | X | |
| General apron | |||
| Latex gloves | |||
| Fine dust mask | X | ||
| Breathing protection with filter* | |||
| Ear defenders | X | ||
| Welding apron, clothing suitable for welding | X | X | |
| Welding shield, welding mask | X |
*only if there is insufficient ventilation
The up-to-date guidelines and notes in the workshop information system ISTA must always be observed. In addition to the general protective equipment, country-specific provisions must also be complied with where applicable.
Working area
A safe and high-quality working environment requires cleanliness and order. When processing steel components, workers must always not only ensure that they themselves are safe, but also that other work bays and employees are not put at risk.
| Protective equipment | MAG welding | Spot Welding | Sanding / Grinding & Cutting | Bonding |
| Partition walls, protective curtains | X | X | X | |
| Welding emission extraction | X |
A fire extinguisher must always be close to hand during work with a raised level of fire risk for example MAG welding.
The up-to-date guidelines and notes in the workshop information system ISTA must always be observed. In addition to the general protective measures for the working area, country- specific provisions must also be complied with where applicable.
Tools
The general and country-specific safety regulations for work with tools for processing metal must be complied with.
The general safety regulations are:
-
Do not clean tools with compressed air.
-
Do not use abrasives that have already been used for processing aluminum.
-
Always separate tools for steel processing and aluminum processing.
Environment
The proper disposal and recycling of materials are described in the environmental protection law. The laws serve to protect natural resources and preserve the environment. Environmental protection laws are regulated on a market-specific basis.
Recycling
Scrap metals from vehicles are largely recyclable. The steel is added to the steel production process.
To separate the various materials in the body shell, the body shell is compressed into a bundle and shredded. The shredded material is separated into ferrous metals, non- ferrous metals and other materials. This is done with the sink-float method using their different weights.
After jacking up a vehicle body, be sure to support it with the safety stand. For the supporting positions, refer to “Lifting Points” in the Service Manual for each model.
-
Before starting repair work, be sure to disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
-
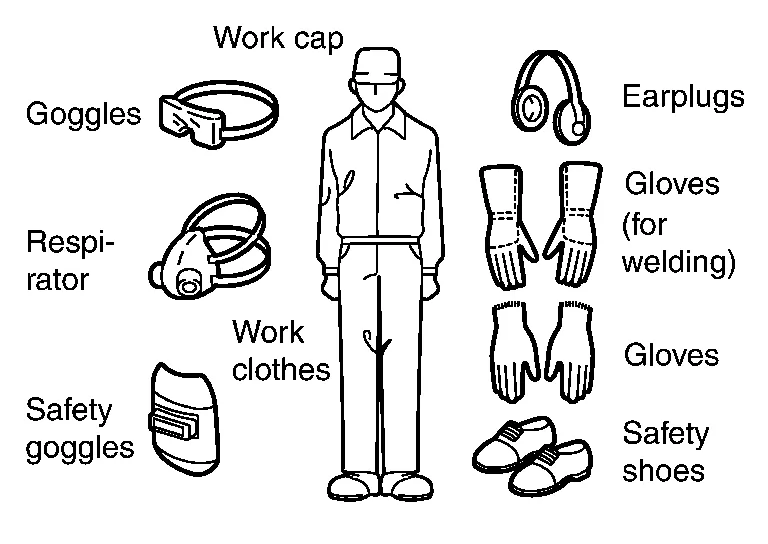
When welding parts near the fuel tank fuel filler, be sure to remove the fuel tank. Plug the filler port of the tank.
-
Plug the fuel pipe and brake pipes to avoid leakage when removing connectors from the pipes.
-
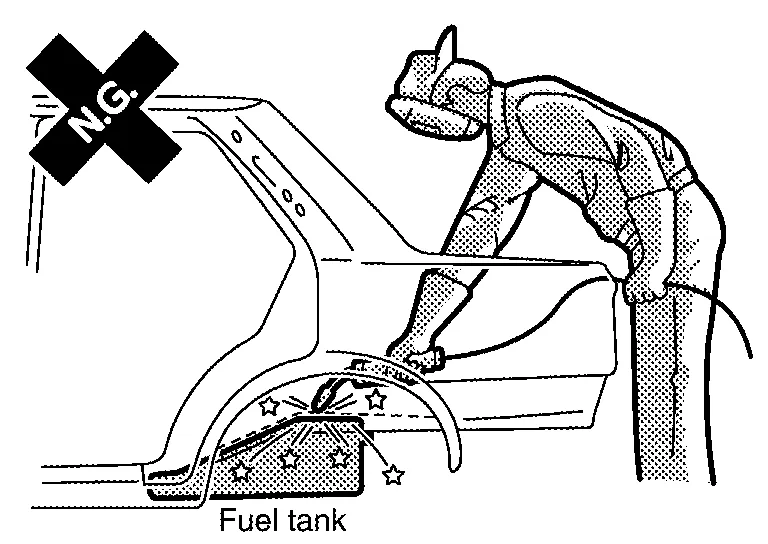
Pay attention to ventilation and the health of workers.
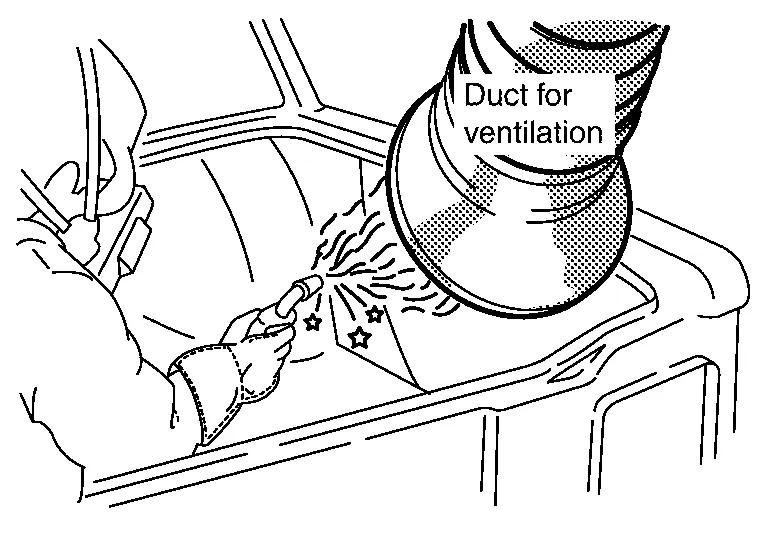
-
Paint and sealant may generate poisonous gases when heated by fire. To prevent this, do not use a gas welder for cutting off damaged portions.
-
Use an air saw or an air chisel.
-
Use a belt sander or rotary wire brush for removing paint from the panel.
(1) STORAGE OF GAS CYLINDERS
-
In a well ventilated area, post a “No Fire” sign.

-
Avoid the direct rays of the sun. Maintain temperature below 40°C (104°F).
-
Inflammable gas cylinders and oxygen cylinders must not be stored in the same place.
-
Acetylene cylinders must be stored upright. Check that they cannot fall down.
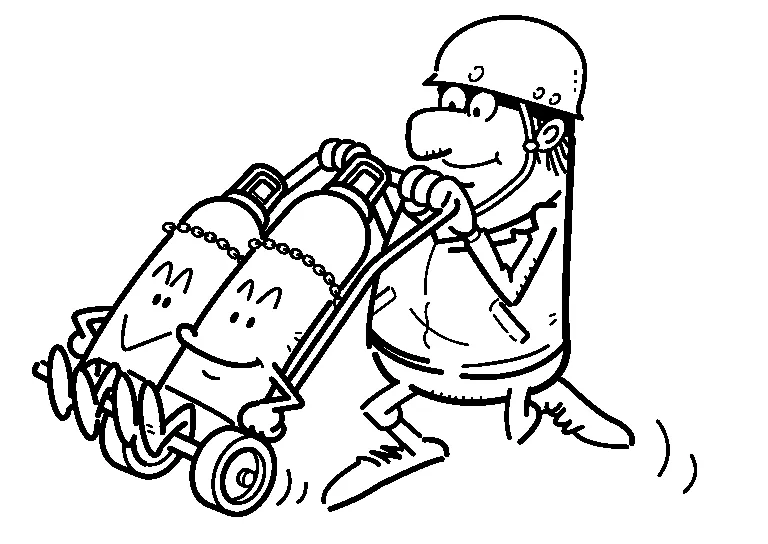
(2) MOVEMENT AND TRANSPORTATION OF CYLINDERS
-
Be sure to properly close the valve and securely install the cap.
-
Do not drag or roll the cylinder.
-
Use a cylinder transportation cart.
-
When moving, tilt the cylinder slightly and roll it carefully on the bottom edge with one hand while supporting its cap with the other hand.
(3) USE OF CYLINDERS
-
The cylinder valve must be kept clean and free from oil.
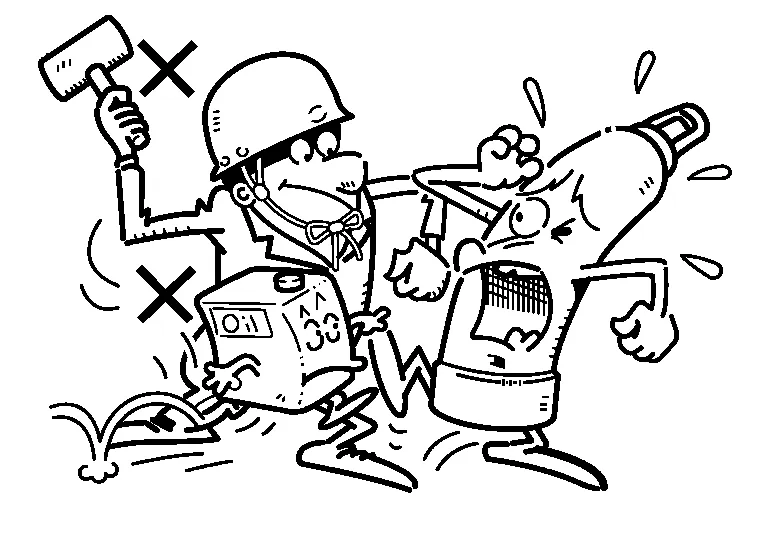

-
After opening the cylinder, leave the open-end wrench attached to the valve so it can be turned off quickly in an emergency.
-
When the cylinder is replaced, open the valve of the new cylinder slightly and remove dust from around the valve seat.
-
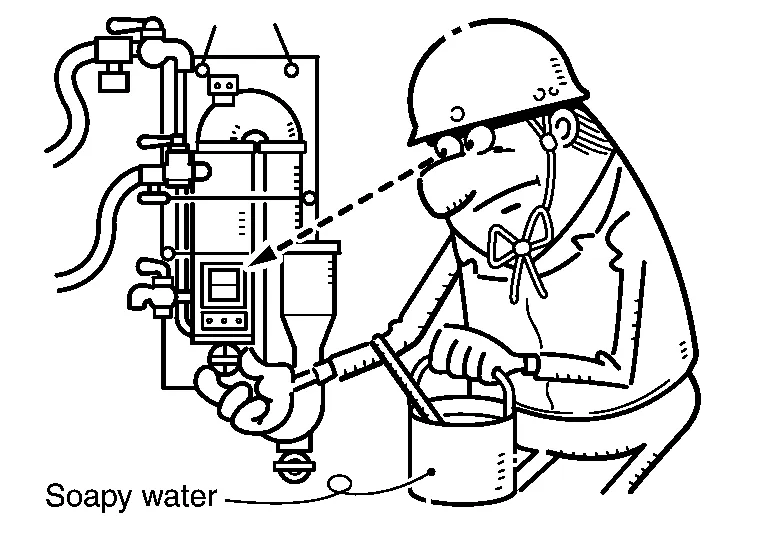
To check the cylinder for leakage, apply soapy water.
-
The valve should be fully open for oxygen and open 1.5 turns or so for acetylene.
-
To prevent the cylinder from falling down, ensure that it is properly secured.
-
And never give a shock to the cylinder.
(4) HANDLING OF THE PRESSURE REGULATOR
-
Always handle the pressure regulator with care and avoid impact.
-
Inspect the regulator periodically (at least once a year).
-
After use, purge the gas, and set the gauge to “0” (except the indoor type pressure regulator).
(5) HANDLING OF WATER-SEALED SAFETY DEVICES
-
This device must be installed vertically. Check the water level every morning.
-
In case of freezing, antifreeze solution can be added.
(6) HANDLING OF HOSES
-
All hoses must be checked before use for flaws or leaks.
-
Never use the pipe coupling made of copper or 70% copper alloy for the acetylene hose.
-
Do not use compressed oxygen to clean the gas hose.
-
Do not use any hose that has experienced backfire.
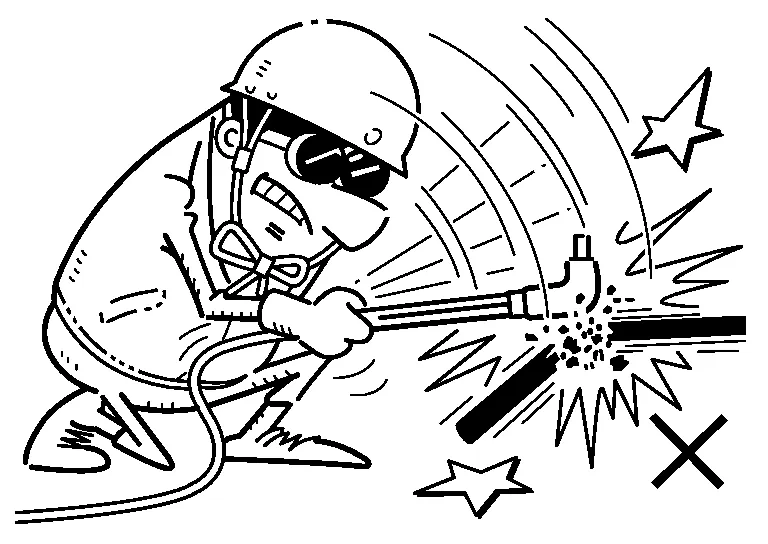
(7) HANDLING OF THE TORCH
-
Keep the torch clean and free from oil.
-
To replace the nozzle, use a special tool.
-
Do not use the torch as a hammer, etc..
-
Do not place it directly on the ground or on the floor.
-
Check suction of the torch at the end of the inflammable gas pipe coupling.
(8) DANGER OF ARC WELDING ELECTRICAL SHOCK
-
Keep cables and connections in good shape.
-
Do not place machine in a wet place. Do not stand in a wet place when welding.
-
Electrically ground welder. The vise clamp is not an electrical ground connection.
 Working with Body Straightening Equipment
Working with Body Straightening Equipment
Use of Protectors
Use of work clothes should be the same as for “PROTECTORS”. Refer to Protectors.
Wear a safety helmet and safety shoes.
When working under a Nissan Murano vehicle or when using a grinder, wear goggles...
Other information:
Nissan Murano (Z52) 2015-2024 Service Manual: Precaution. Precautions
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER" The Supplemental Restraint System such as “AIR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER”, used along with a front seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain types of collisions...
Nissan Murano (Z52) 2015-2024 Owners Manual: Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) (if so equipped)
WARNING Failure to follow the warnings and instructions for proper use of the RCTA system could result in serious injury or death. The RCTA system is not a replacement for proper driving procedures and is not designed to prevent contact with vehicles or objects...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Nissan Murano Owners Manual
- Nissan Murano Service Manual
- System malfunction
- Settings
- Fuel recommendation
- New on site
- Most important about car
LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for CHildren) system
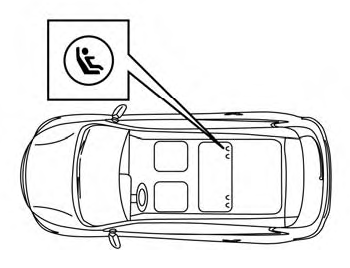
LATCH system lower anchor locations - bench seat
Your vehicle is equipped with special anchor points that are used with LATCH system compatible child restraints. This system may also be referred to as the ISOFIX or ISOFIX compatible system. With this system, you do not have to use a vehicle seat belt to secure the child restraint unless the combined weight of the child and child restraint exceeds 65 lbs. (29.5 kg). If the combined weight of the child and child restraint is greater than 65 lbs. (29.5 kg), use the vehicle’s seat belt (not the lower anchors) to install the child restraint. Be sure to follow the child restraint manufacturer’s instructions for installation.