Nissan Murano: System / Multiport Fuel Injection System
SYSTEM DIAGRAM

*1: ECM determines the start signal status by the signals of engine speed and battery voltage.
*2: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The amount of fuel injected from the fuel injector is determined by the ECM. The ECM controls the length of time the valve remains open (injection pulse duration). The amount of fuel injected is a program value in the ECM memory. The program value is preset by engine operating conditions. These conditions are determined by input signals (for engine speed and intake air) from the crankshaft position sensor (POS), camshaft position sensor (PHASE) and the mass air flow sensor.
VARIOUS FUEL INJECTION INCREASE/DECREASE COMPENSATION
In addition, the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance under various operating conditions as listed below.
<Fuel increase>
-
During warm-up
-
When starting the engine
-
During acceleration
-
Hot-engine operation
-
When selector lever position is changed from N to D
-
High-load, high-speed operation
<Fuel decrease>
-
During deceleration
-
During high engine speed operation
MIXTURE RATIO FEEDBACK CONTROL (CLOSED LOOP CONTROL)

The mixture ratio feedback system provides the best air-fuel mixture ratio for drive ability and emission control. The three way catalyst (manifold) can better reduce CO, HC and NOx emissions. This system uses A/F sensor 1 in the exhaust manifold to monitor whether the engine operation is rich or lean. The ECM adjusts the injection pulse width according to the sensor voltage signal. For more information about A/F sensor 1, refer to Air Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor . This maintains the mixture ratio within the range of stoichiometric (ideal air-fuel mixture).
This stage is referred to as the closed loop control condition.
Heated oxygen sensor 2 is located downstream of the three way catalyst (manifold). Even if the switching characteristics of A/F sensor 1 shift, the air-fuel ratio is controlled to stoichiometric by the signal from heated oxygen sensor 2.
-
Open Loop Control
The open loop system condition refers to when the ECM detects any of the following conditions. Feedback control stops in order to maintain stabilized fuel combustion.
-
Deceleration and acceleration
-
High-load, high-speed operation
-
Malfunction of A/F sensor 1 or its circuit
-
Insufficient activation of A/F sensor 1 at low engine coolant temperature
-
High engine coolant temperature
-
During warm-up
-
After shifting from N to D
-
When starting the engine
-
MIXTURE RATIO SELF-LEARNING CONTROL
The mixture ratio feedback control system monitors the mixture ratio signal transmitted from A/F sensor 1. This feedback signal is then sent to the ECM. The ECM controls the basic mixture ratio as close to the theoretical mixture ratio as possible. However, the basic mixture ratio is not necessarily controlled as originally designed. Both manufacturing differences (i.e., mass air flow sensor hot wire) and characteristic changes during operation (i.e., fuel injector clogging) directly affect mixture ratio.
Accordingly, the difference between the basic and theoretical mixture ratios is monitored in this system. This is then computed in terms of “injection pulse duration” to automatically compensate for the difference between the two ratios.
“Fuel trim” refers to the feedback compensation value compared against the basic injection duration. Fuel trim includes “short-term fuel trim” and “long-term fuel trim”.
“Short-term fuel trim” is the short-term fuel compensation used to maintain the mixture ratio at its theoretical value. The signal from A/F sensor 1 indicates whether the mixture ratio is RICH or LEAN compared to the theoretical value. The signal then triggers a reduction in fuel volume if the mixture ratio is rich, and an increase in fuel volume if it is lean.
“Long-term fuel trim” is overall fuel compensation carried out over time to compensate for continual deviation of the “short-term fuel trim” from the central value. Continual deviation will occur due to individual engine differences, wear over time and changes in the usage environment.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING

Two types of systems are used.
-
Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System
Fuel is injected into each cylinder during each engine cycle according to the ignition order. This system is used when the engine is running.
-
Simultaneous Multiport Fuel Injection System
Fuel is injected simultaneously into all six cylinders twice each engine cycle. In other words, pulse signals of the same width are simultaneously transmitted from the ECM.
The six injectors will then receive the signals 2 times for each engine cycle.
This system is used when the engine is being started and/or if the fail-safe system (CPU) is operating.
FUEL SHUT-OFF
Fuel to each cylinder is cut off during deceleration, operation of the engine at excessively high speeds or operation of the Nissan Murano vehicle at excessively high speeds.
 Engine Control System
Engine Control System
System Description
SYSTEM DIAGRAMSYSTEM DESCRIPTIONECM controls the engine by various functions. Function Reference
Multiport fuel injection system
System Description
Electric ignition system
System Description
Air conditioning cut control
System Description
Automatic speed control device (ASCD)
System DescriptionSystem Description
Cooling fan control
System Description
Electronic controlled engine mount
System Description
Evaporative emission system
System Description
Throttle control
System Description
Intake valve timing control
System Description
Exhaust valve timing control
System Description
Engine protection control at low engine oil pressure
System Description
Fuel filler cap warning system
System Description
Variable induction air system
System Description
Integrated control of engine, CVT, and ABS
System Description
CAN communication
System Description
Fuel pump control module (FPCM)
System Description
Fail-safe
DTC No...
 Electric Ignition System
Electric Ignition System
System Description
SYSTEM DIAGRAM*: ECM determines the start signal status by the signals of engine speed and battery voltage.SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONIgnition order: 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6The ignition timing is controlled by the ECM to maintain the best air-fuel ratio for every running condition of the engine...
Other information:
Nissan Murano (Z52) 2015-2024 Service Manual: Microphone
Removal and Installation REMOVALRemove the map lamp assembly. Refer to Removal and Installation. Remove the microphone connector from the map lamp assembly . Release the microphone pawls, then remove the microphone . : Pawl INSTALLATIONInstallation is in the reverse order of removal...
Nissan Murano (Z52) 2015-2024 Service Manual: System. Power Supply, Ground & Circuit Elements
Circuit Breaker (Built Into BCM) For example, when current is 30A, the circuit is broken within 8 to 20 seconds.This circuit breaker is used for the following systems: Power windows Power moonroof Power seat Power lumbar Power sunshade Circuit Breaker (External to BCM) The PTC thermistor generates heat in response to current flow...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Nissan Murano Owners Manual
- Nissan Murano Service Manual
- Rear bench seat adjustment
- Warning lights
- Jacking up vehicle and removing the damaged tire
- New on site
- Most important about car
Luggage hooks
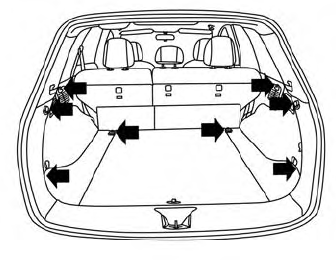
When securing items using luggage hooks located on the back of the seat or side finisher do not apply a load over more than 6.5 lbs. (29 N) to a single hook.
The luggage hooks that are located on the floor should have loads less than 110 lbs. (490 N) to a single hook.