Nissan Murano: Repairing Procedures and Precautions / Damage Diagnosis
What is force
Force causes the shape of objects and state of motion to change.
-
Equation that expresses force [F]
-
F= m + a
-
[m: mass in kg, a: rate of acceleration in m/s2]
The equation explains the factors that affect the force strength in a collision. The impact force is in relation to the mass and the rate of acceleration or deceleration of a Nissan Murano vehicle.
In a collision a vehicle is damage is by the force which is applied on the vehicle. The force causes the shape of the Nissan Murano vehicle to change as the force changes the state of motion it is in. There are 5 elements in force to consider.
The five elements of force
There are 3 main force elements, size, direction and application point. In damage diagnosis it is important to understand these as well by adding 2 more aspects of "number of impacts" and the "sequence of impact".
Please see below explanation in details:
| The Three Main Elements | 1. Force Size |
| 2. Force Direction | |
| 3. Force Application Point |
| Further aspects | 1. Size is shown through the length |
2. Direction by arrow  |
|
| 3. Application point by tip | |
| 4. Force Number of Impact | |
| 5. Force Sequence of the Impacts |
-
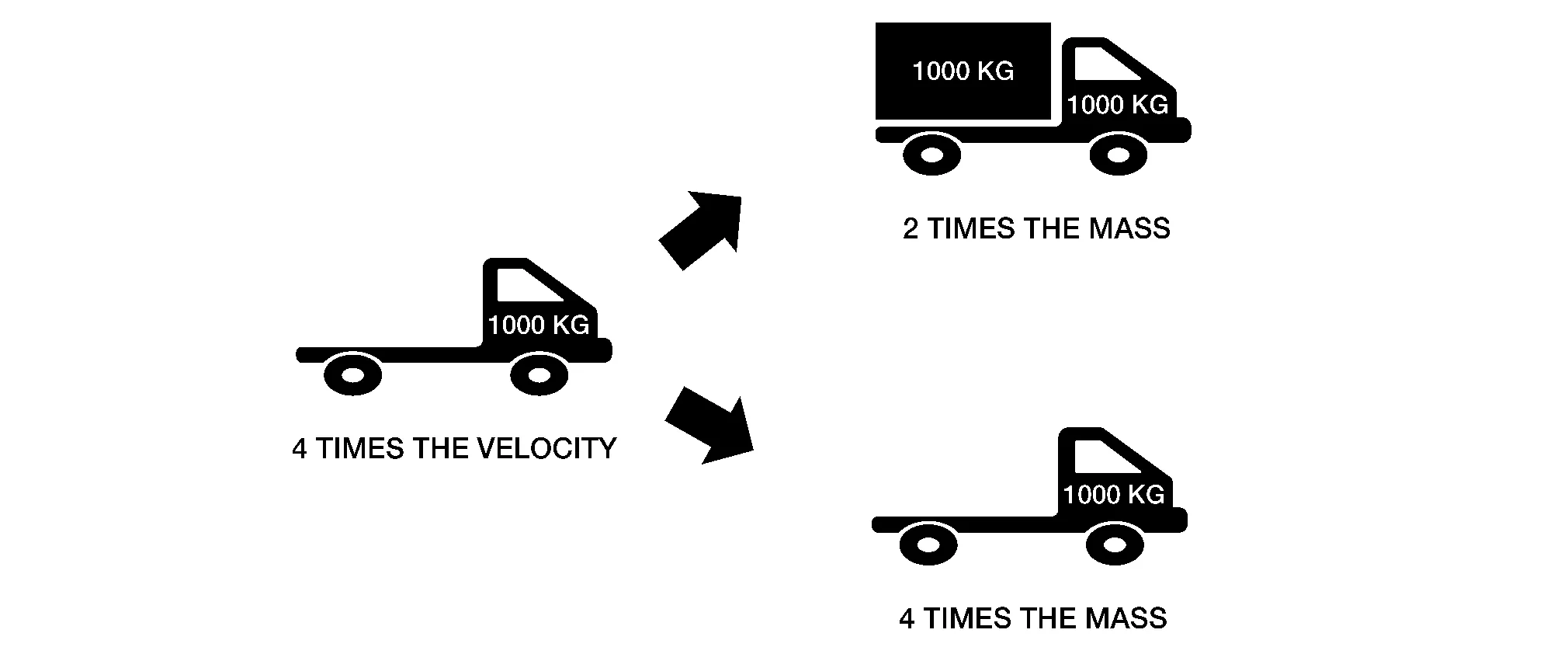
Equation that expresses kinetic energy [EK]
-
EK = 1/2 ● m ● v2
-
[m: mass in kg, v: velocity in m/s]
The equation shows that the kinetic energy is proportional to the mass and the square of velocity. In an accident, not all of this kinetic energy will be absorbed as damage to Nissan Murano vehicle or the other object.
The energy of the object gets transformed into different energy as well as heat, sound, friction and change in the Nissan Murano vehicles position by spinning.
Depending on the amount of force acting on an object on a vehicle construction will depend on how far the absorption will be in the Nissan Murano vehicle body structure.
We will be looking at force and different types of deformations that can occur on an object, part or structure.
Elastic Deformation
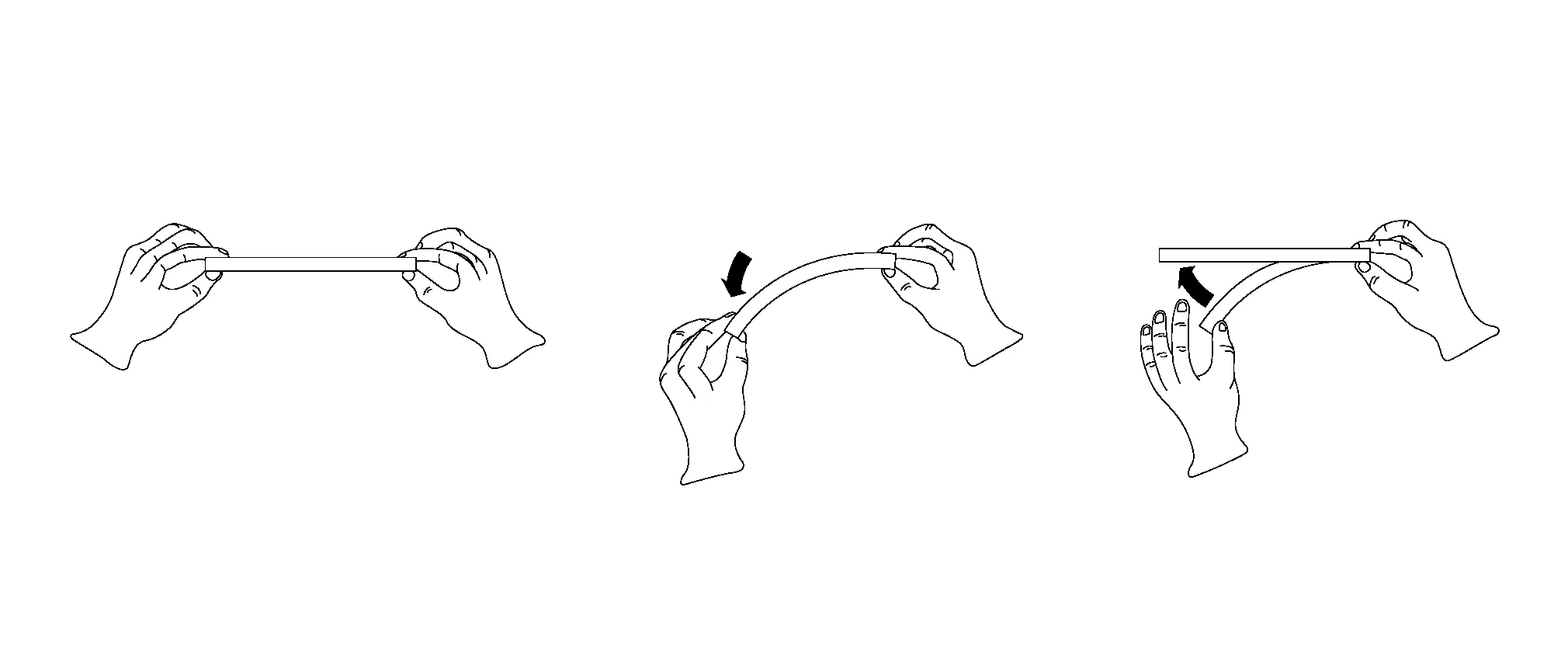
If you apply light force to a panel and it deforms lightly, and once released. it returns to its original shape or form, this is called elastic deformation. If the panel gets elastically deformed. it will always return to its original shape or form. This means that stretching has occurred. The material has not gone past its yield strength.
Plastic Deformation
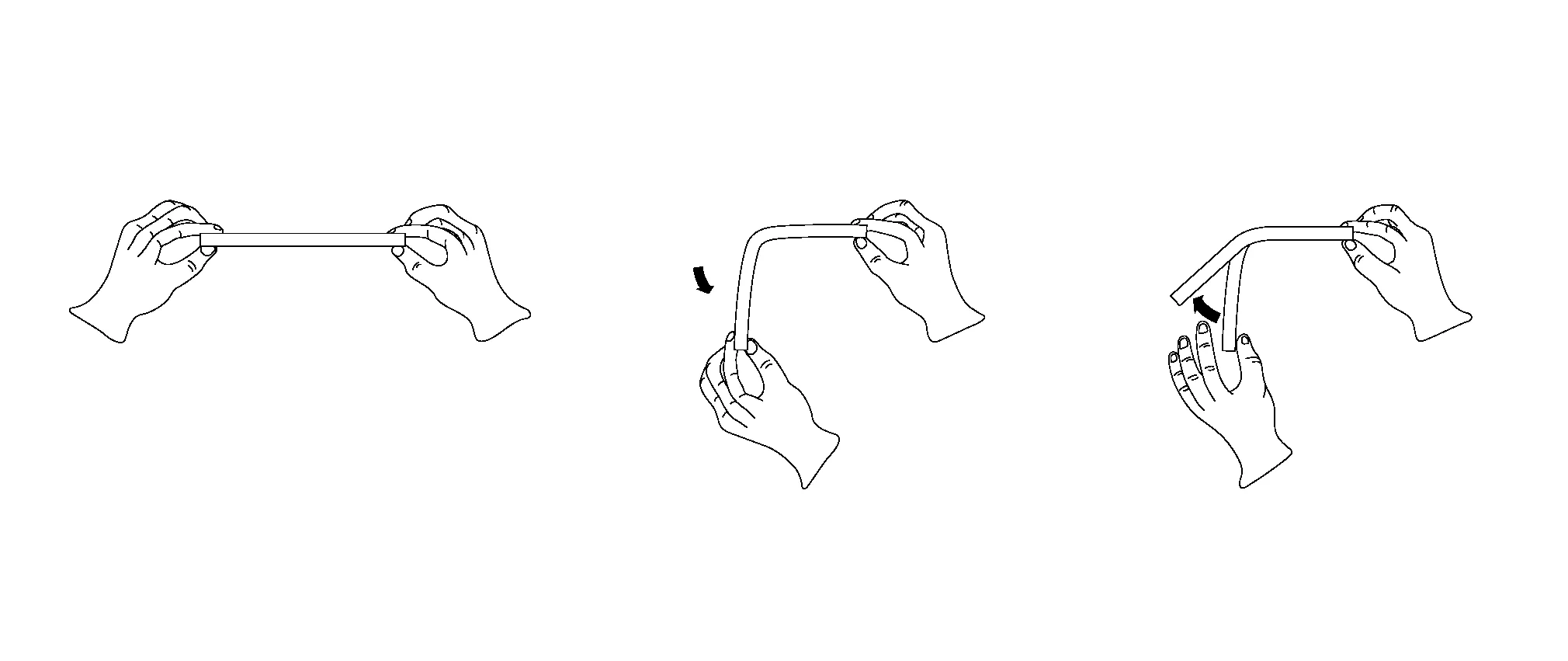
If you apply force to a panel and it deforms, and once released it does not return to its original shape, the piece has been plastically deformed. This is called plastic deformation. The point of bending of the material means that it has gone past its yield strength. In most sharp damages the centre of the impact area has been plastically deformed.
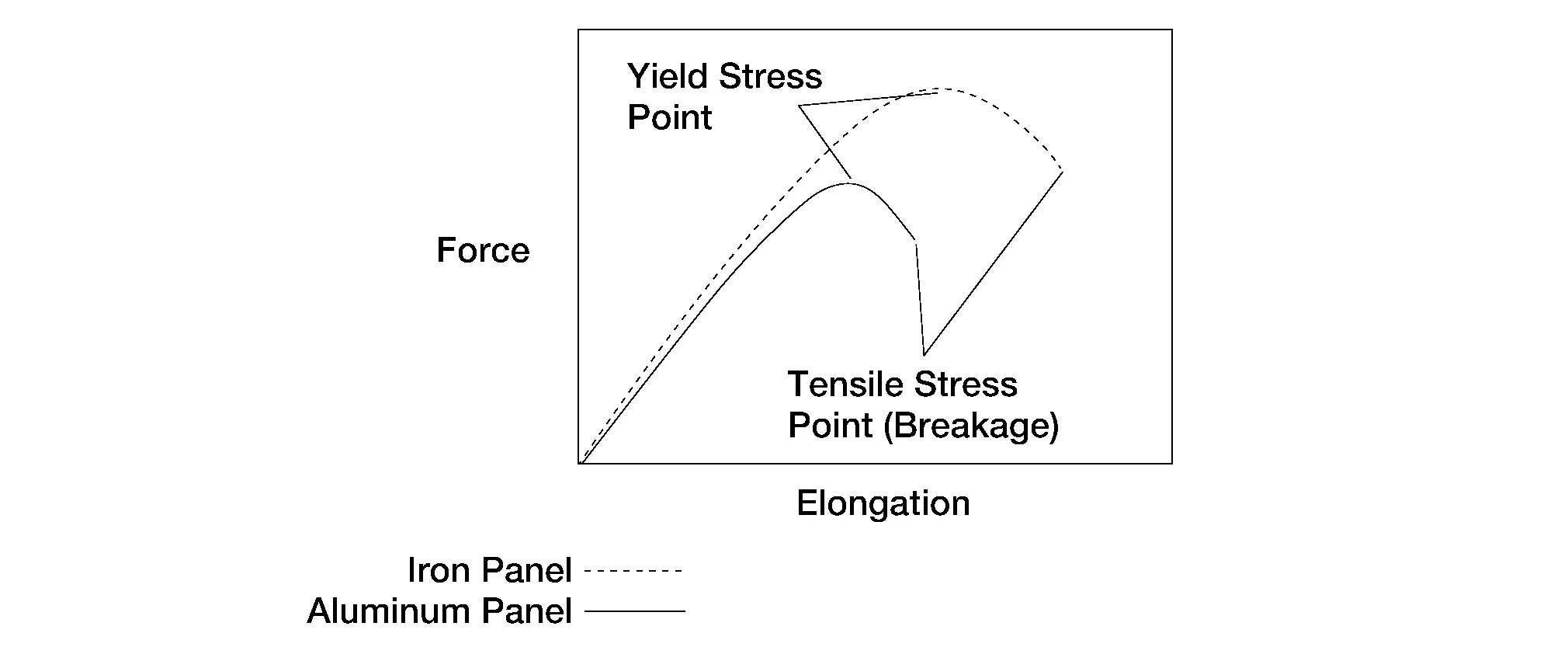
This graph shows the strength in relation to elongation of material.
Point three shows the tensile strength point. At this point the material starts to be plastically deformed.
Deformation occurs when force is applied on an object and the generated stress exceeds the limit within which the object can maintain its shape.
Here, we will explain about the force applied on objects and the deformation that occur on objects.
Examples below show the type of deformation on a shape or object.
Crumpling
Crumpling occurs when a force acts on an object straight on, and if the shape has an equal shape and strength.
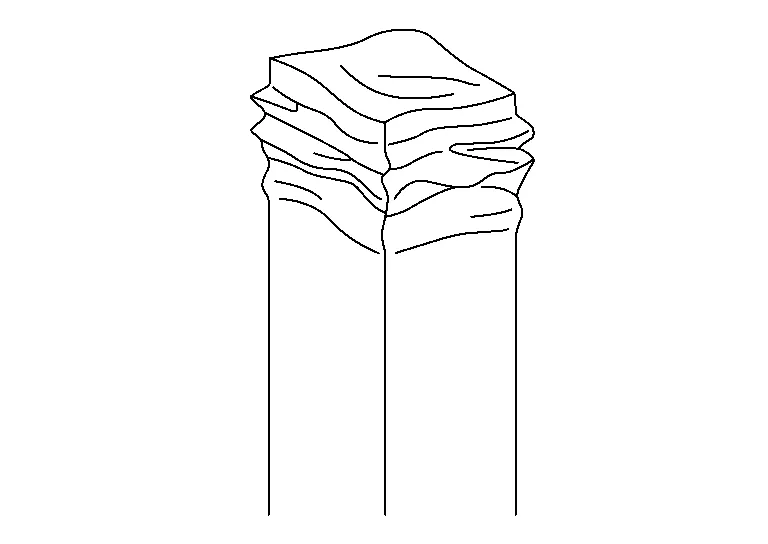
Bending
Bending is a deformation that can be either one sided, an angled pull or push. It mainly occurs in induced damages. Since the bend is not always very visual it can be difficult to be detected. By removing the direct impart parts it can also return to its original shape due to elastic deformation. This will depend on the force and material as well.
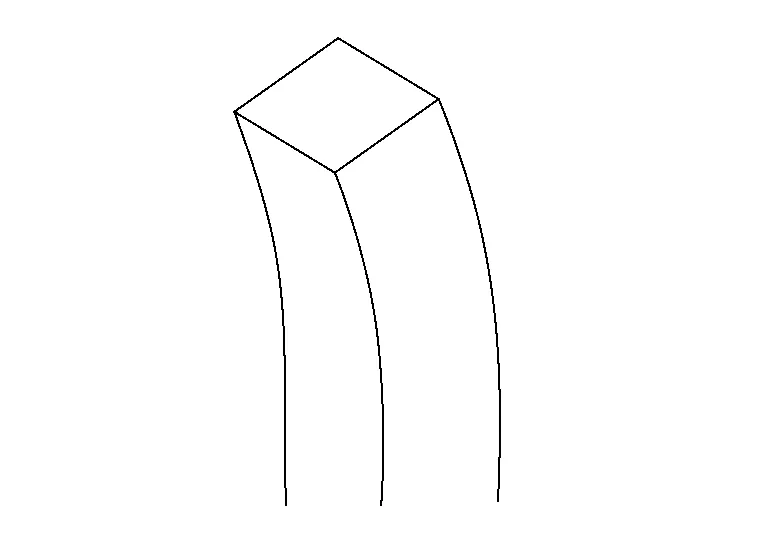
Folding
Folding occurs if a larger force is applied to an object or part which has gone past its yield strength. It is also caused if a force comes from an angle or a side.
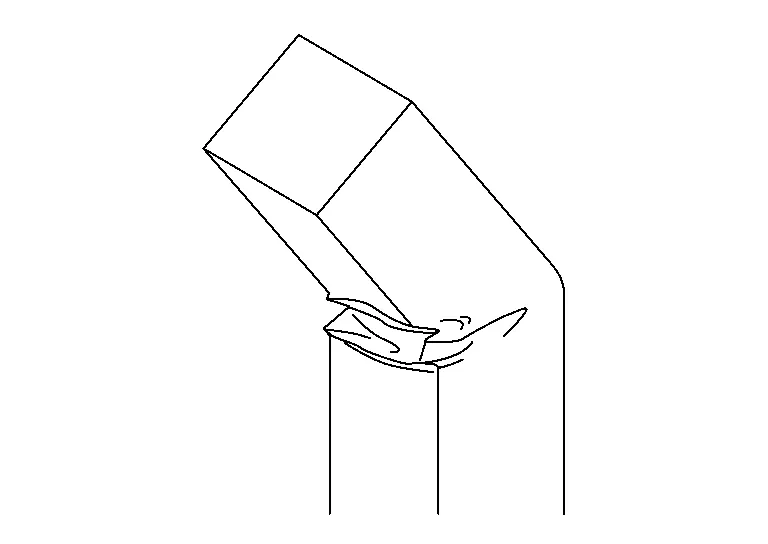
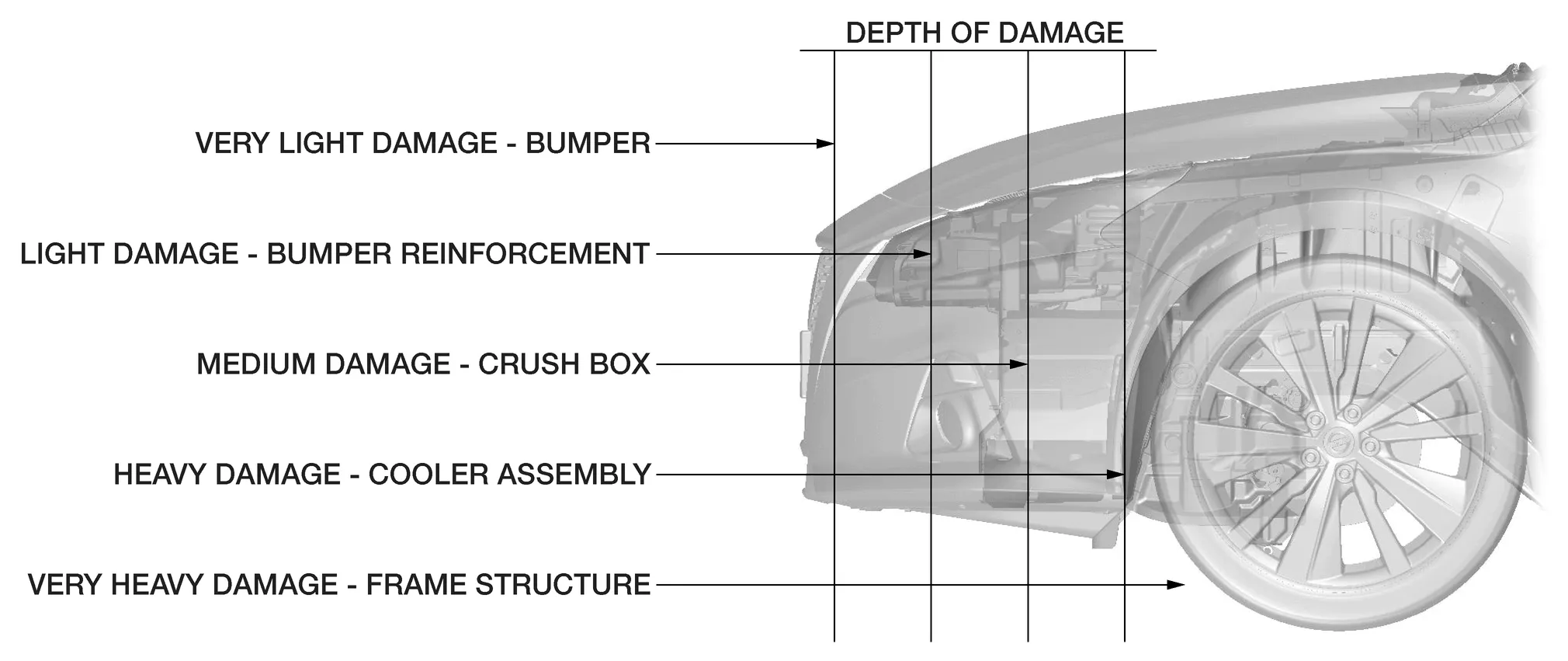
Range or extent of Damage
Recognize the extent of the damage for the entire vehicle and each part to understand the overall extent of damage from the two viewpoints of "the extent of damage to the out panels and exterior parts" and "extent of damage to the inner panels and frame.
-
Extent of Damage for Outer Panels & Exterior Parts .
Inspect from what area or part and to which area or part the direct or indirect damage has occurred including its surroundings
-
Extent of Damage for Inner Panels & Frame
Inspect deeper in to the inner parts which were caused by the direct damage and indirect damage to the inner panels and frame parts.
Level of Damage
After recognizing the extent of the damage to the whole vehicle, inspect the level of damage by looking for bends, dents, cracks, deformations, waves or twisted parts in individual parts or areas.
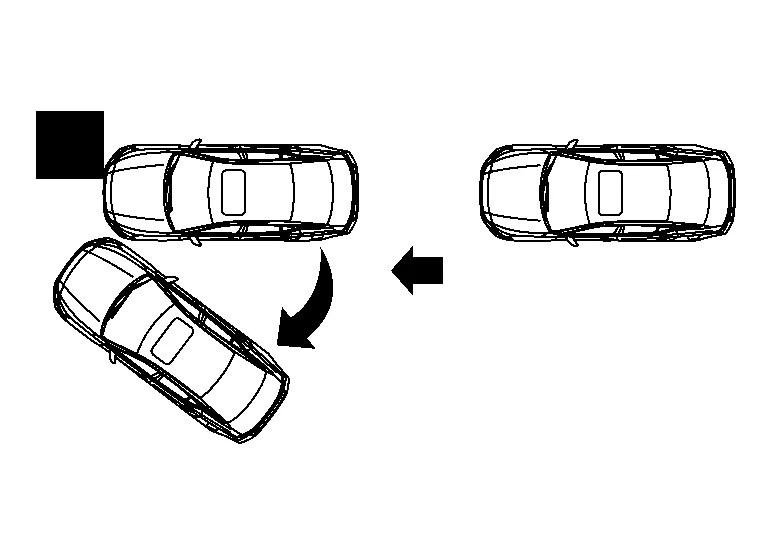
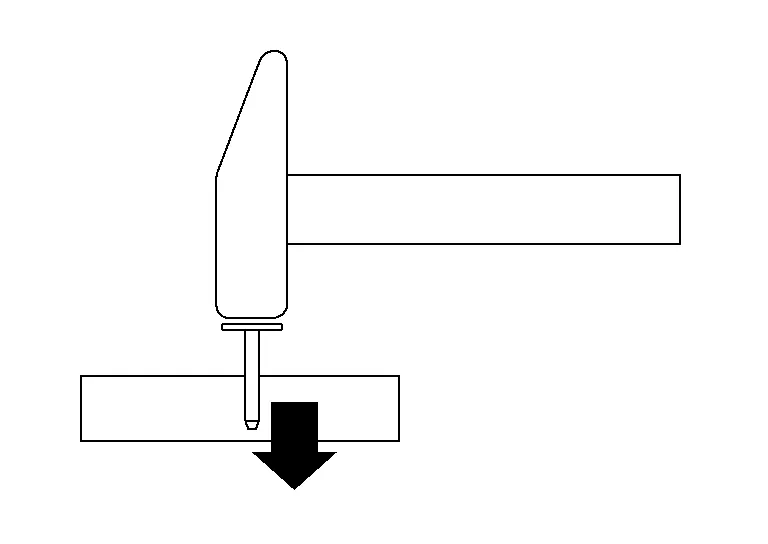
We will look at the different forces acting on part deformations according to the direction the force is applied considering the three elements of force. We will be looking at the basics with a hammer and nail.
Direct Force
The force is applied directly perpendicular to the panel or part.
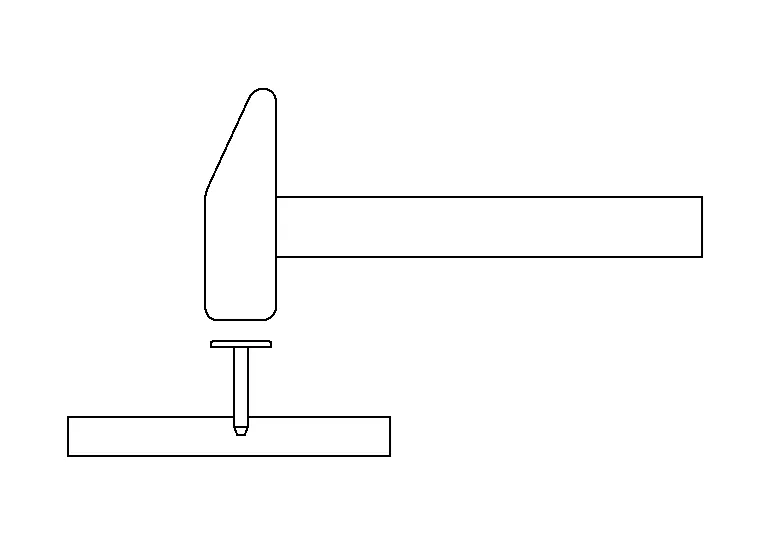
The force will drive the nail straight into the board. If the force is larger, the nail will be driven in deeper.
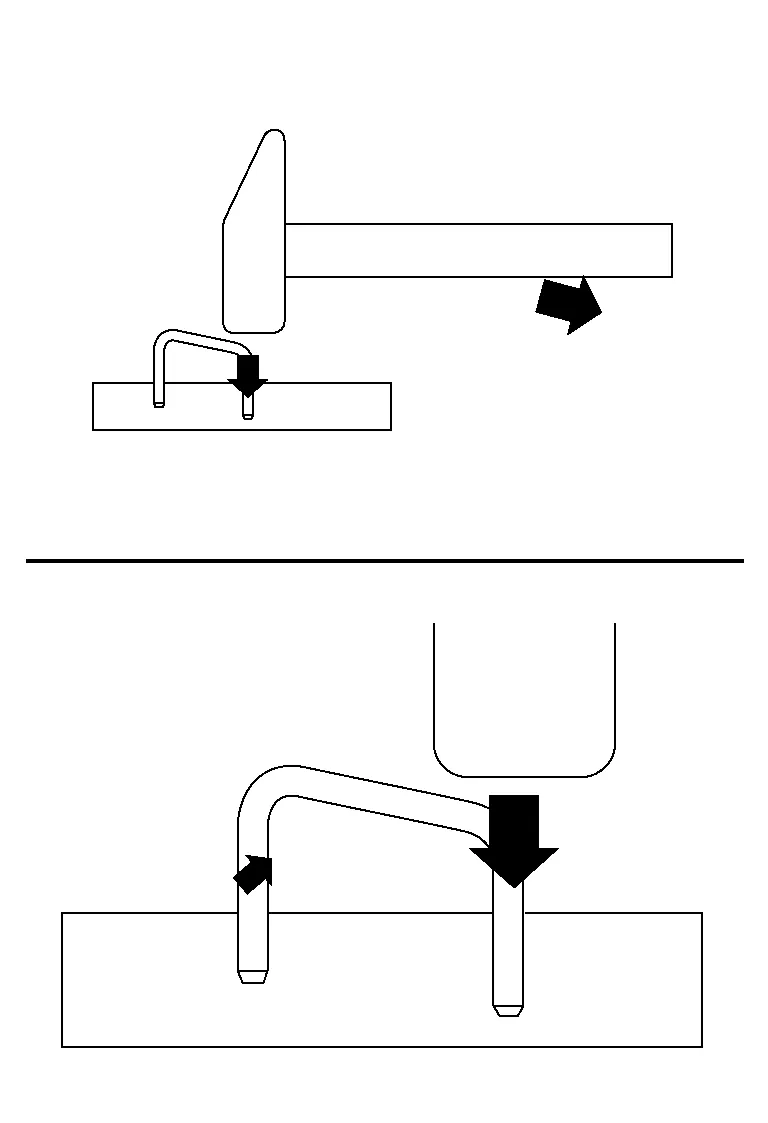
We will now be looking at "U" nails as they are similar to a vehicle s frame shape. If the force is applied to one side of the "U" nail than it will drive one side into the board. However, because the other side is connected, there will also be a pulling force on the other side of the impact area.
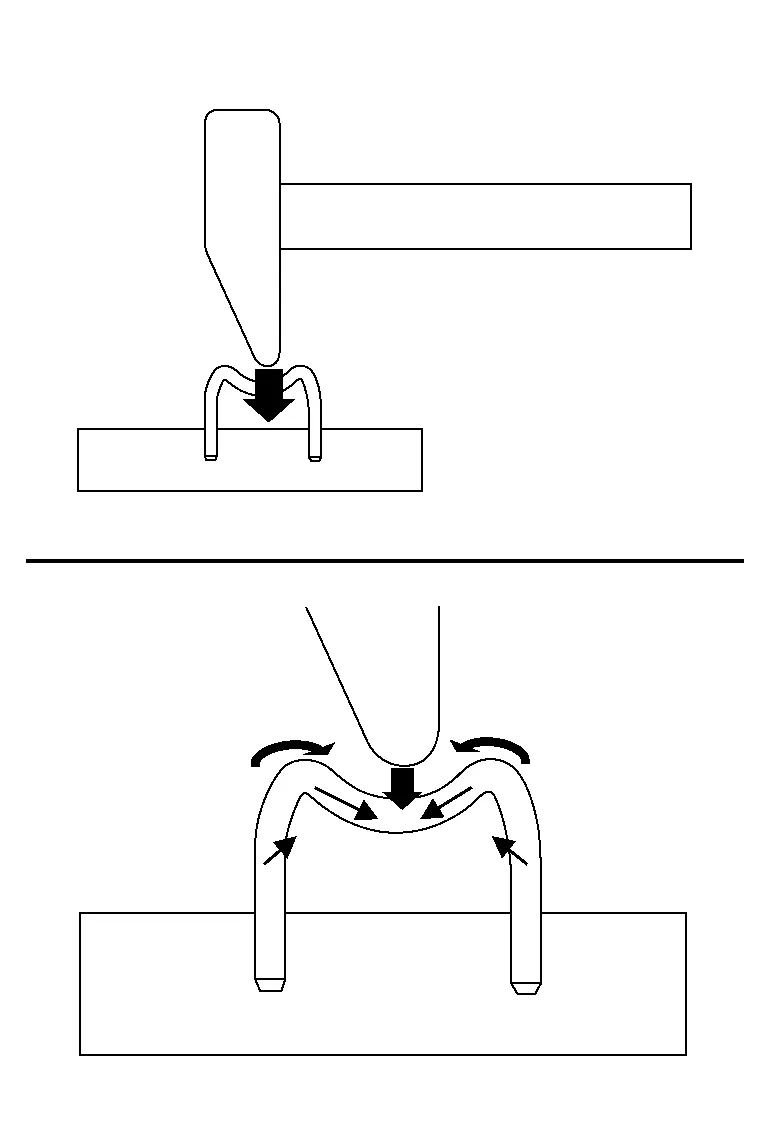
If the force application point is the center of the "U" nail than the pushing force is downward. This will also cause a pulling force laterally on the sides of the "U" nail. At the same time, a further force is acting which tries to drive the left and right sides into the board and causing the nail to drive into the board.
Systematic Approach
A systematic damage diagnosis of the damage condition on a vehicle is very important to get an exact estimate.
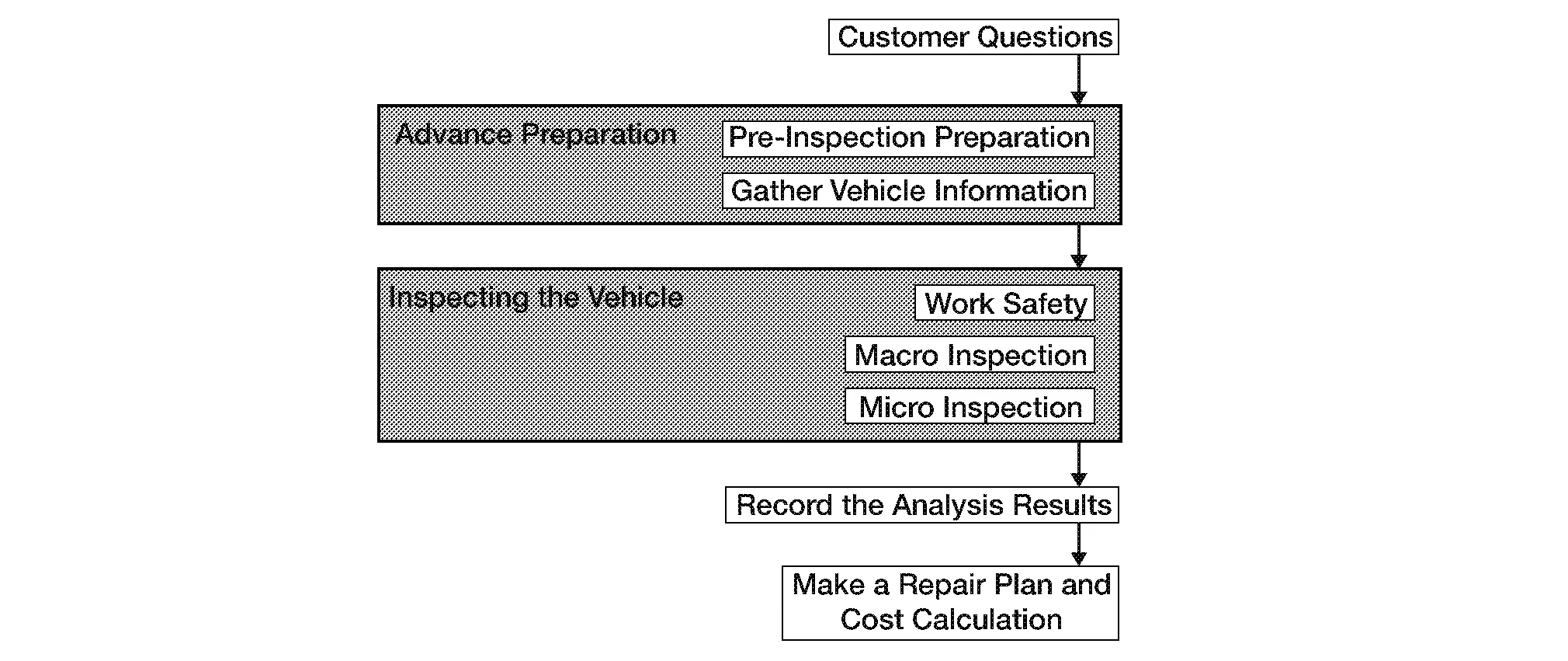
Damage Diagnosis Flow
The method to accurately analysis damage includes macroscopic observations and microscopic observations and uses the following procedure to comprehend the "overall picture of the damage".
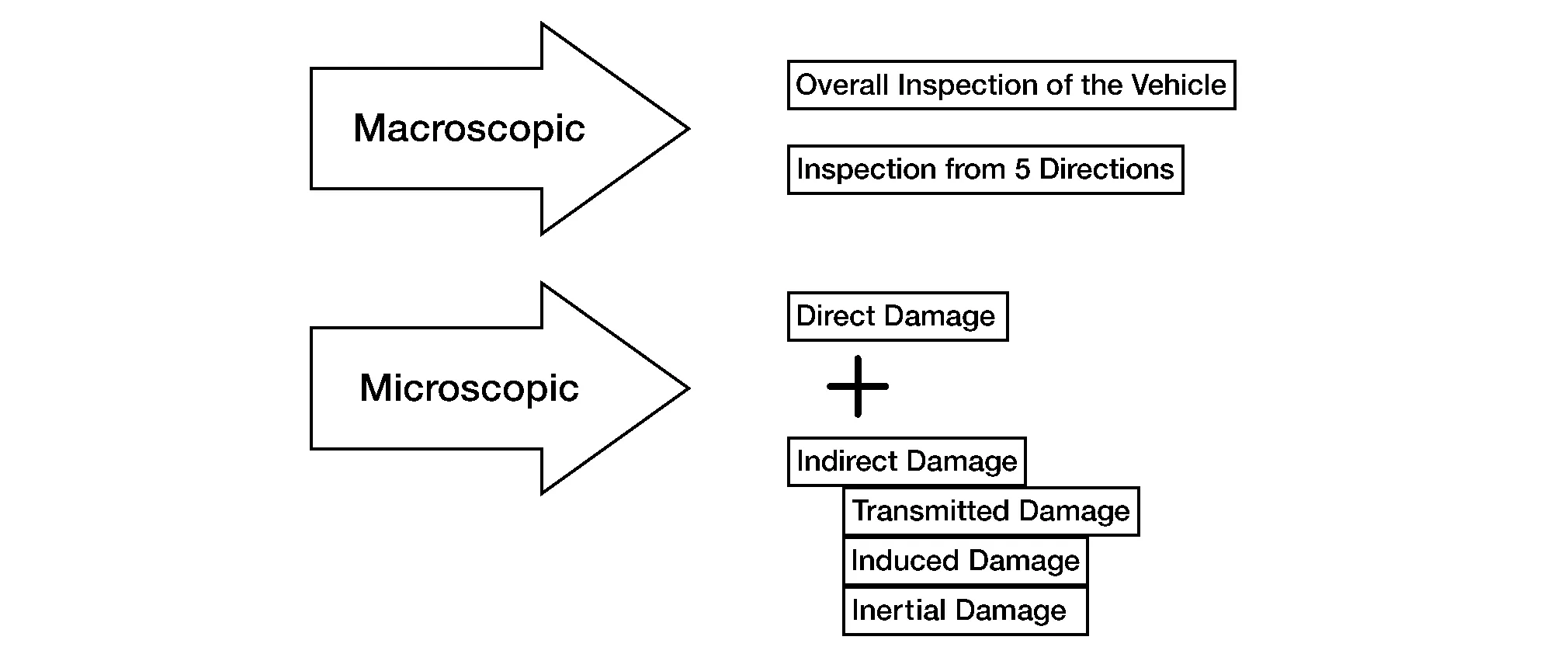
The damage must be diagnosed using the following criteria.
-
Location of damage
-
Range of affected area
-
Degree of damage
These three points relate directly to the quality, efficiency and cost of damage repair, and they must be determined correctly.
-
Size, shape, position, rigidity, etc. of the other vehicle involved in the collision
-
Speed of both Nissan Murano vehicles at the time of collision
-
Collision angle and direction
-
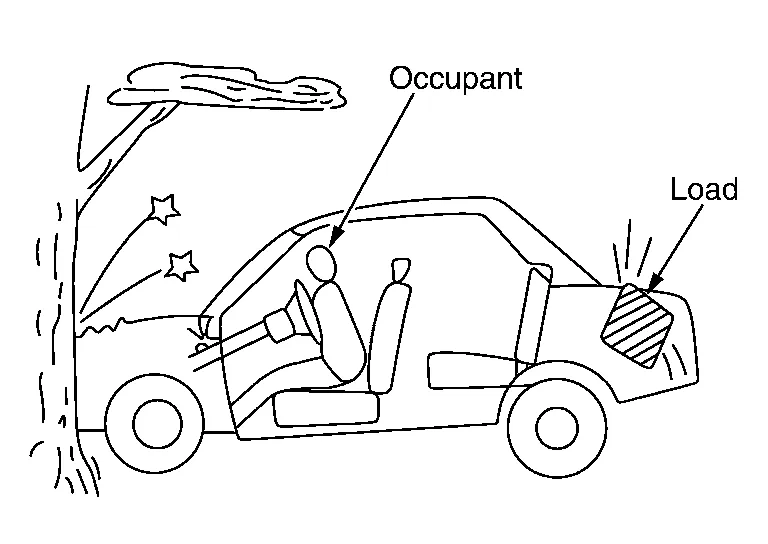
Number of occupants and their positions at the time of collision
-
Size, shape, hardness, etc. of load in the Nissan Murano vehicle
-
History of damaged portion, date of occurrence, and range of affected area
-
Was the Nissan Murano vehicle towing anything
In body repair work, be careful not to overlook indirect damage. To avoid this, mechanical and structural analysis of the Nissan Murano vehicle body is essential.
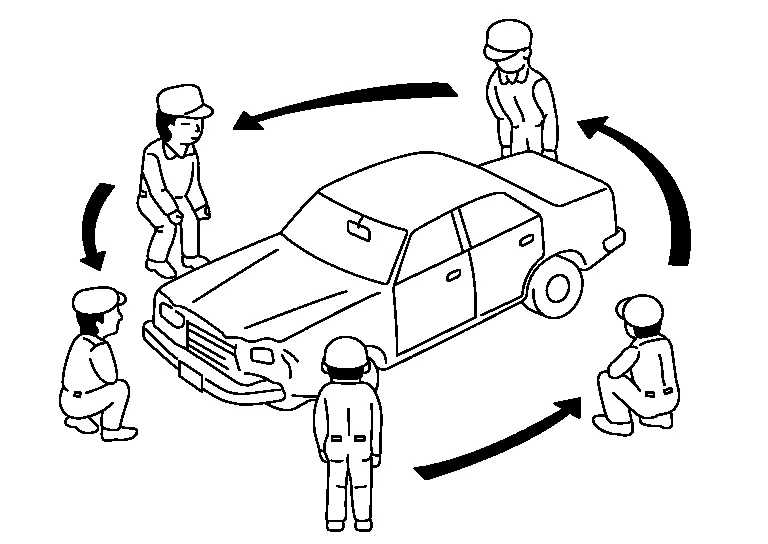
(1) OBSERVATION OF OVERALL VEHICLE
-
The extent of the impact damage
-
Twisting, bending, and inclination of the whole Nissan Murano vehicle
-
Amount and location of damage: Check by examining the whole vehicle
Examples
-
Cracked or stressed paint
-
Cracked or broken glass
-
Broken stressed spot welds
-
Panel separations, deformation
-
Cracked or split seam sealer
-
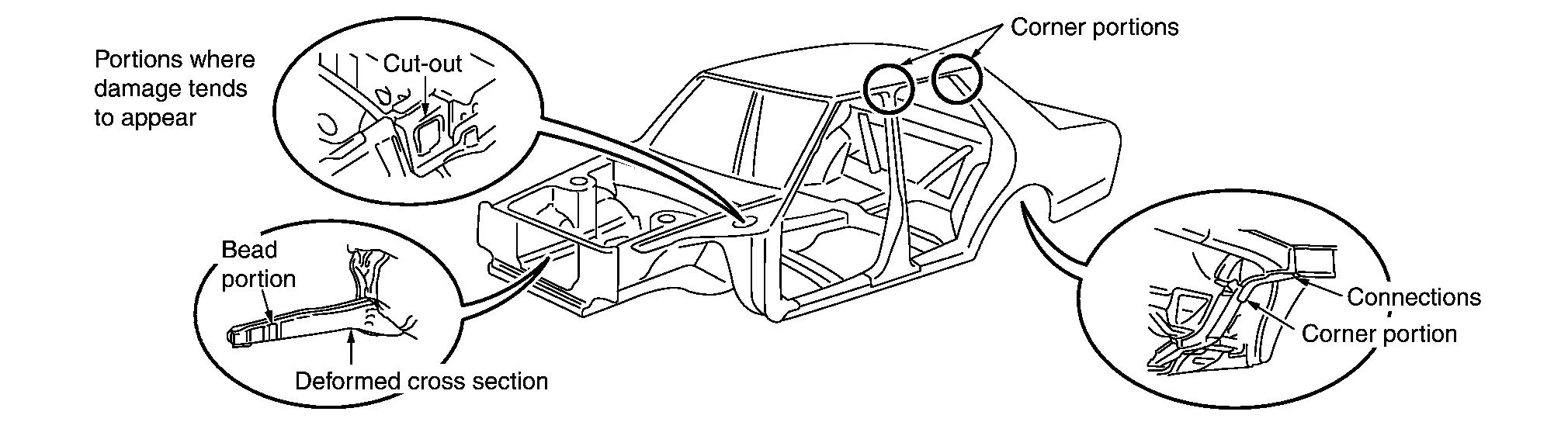
(2) DETAILED OBSERVATION OF VEHICLE
Check for any gaps or dislocation at the welded seams of panels, or cracks in paint film, undercoating or sealing material.
(3) OBSERVATION OF FITTING
Examine the fit of various portions without lifting them.
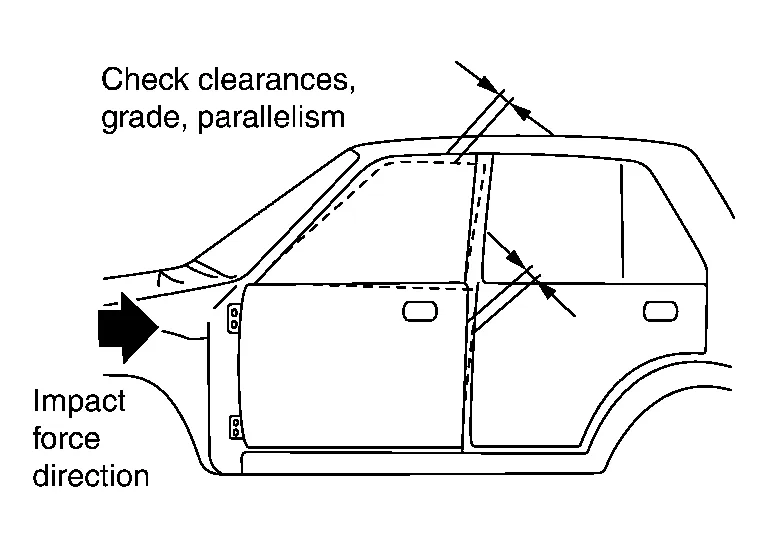
Estimate the damage in the pillar and hinge portions.
-
Door alignment
-
Alignment of hood and trunk lid
-
How doors, hood, and trunk lid open and close
-
Smooth operation of windows
(4) CHECKING FOR MECHANICAL DAMAGE
Damage analysis also involves inspecting mechanical, steering and suspension parts for damage. When inspecting mechanical parts, look for signs of damage such as
-
Bent or damaged parts
-
Fluid leaks
-
Binding or noise when turning the steering wheel
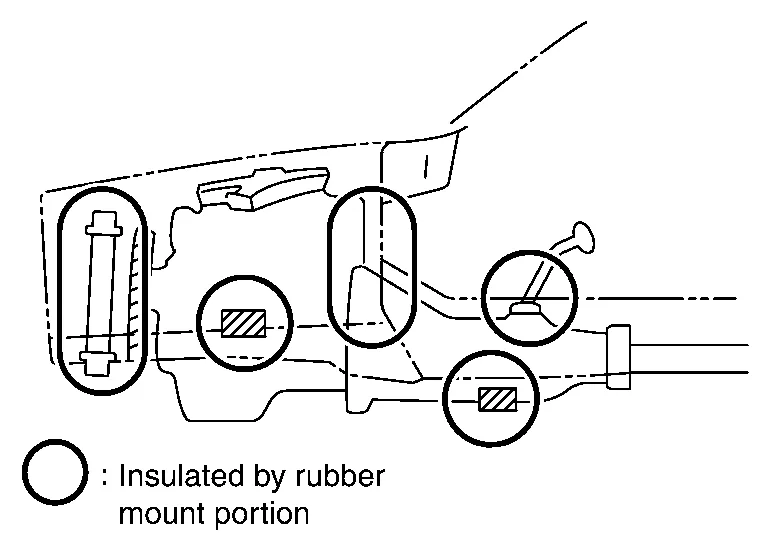
(5) DAMAGE BY INERTIA
Check indirect damage such as a concave roof in frontend collisions, load damage and damage to the engine, which is insulated by rubber mounts.
-
Damaged or misaligned mounting points.
-
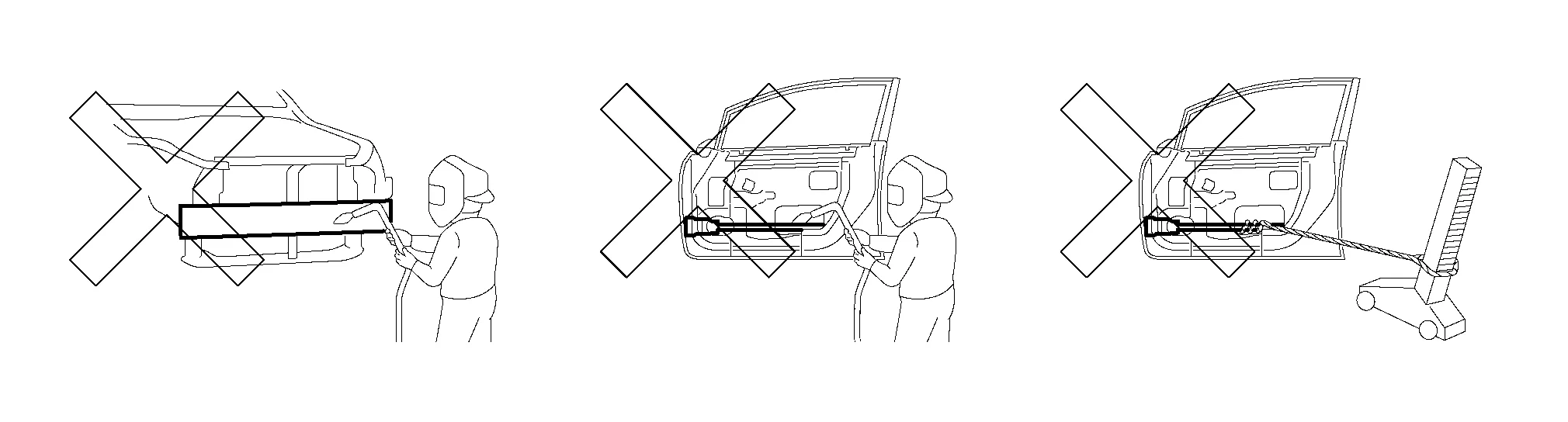
Do not reduce strength when repairing panels. Avoid excessive hammering which may lead to extending the panel.
Also avoid prolonged heating.
-
Do not increase the strength of impact absorbing portions unnecessarily. Do not repair these parts.
-
Choose a method for properly aligning the body.
For example, if changing the front side member of a full frame Nissan Murano vehicle, it is recommended that the front suspension mounting member be left alone.
-
Examine carefully how past collision damage was repaired. This is necessary to properly decide the range to be repaired.
-
Check material (UHSS, Aluminum, etc.) to determine appropriate repair method.
-
High-strength steel parts: The strength of these parts will be reduced if repaired by heating.
-
Parts relating to body alignment and wheel alignment: Replacement of such parts would not provide proper alignment.
-
When repair costs exceed replacement cost.
-
Availability of service parts.
-
When asked by customer.
-
Repair of door side impact beam and bumper reinforcement is prohibited: Beams and reinforcements must be their original shape to perform as designed. Always replace door side impact beams and bumper reinforcements if damaged.
When performing repair work, it is necessary to consider quality, efficiency and cost, as well as safety and health. It is also important to gain the customer's confidence.
 Fundamentals of Body Repair
Fundamentals of Body Repair
Fundamentals of Body Repair
There are many kinds of damage caused by collisions.Therefore, the appropriate repair method for the damage should be selected...
 Checking Damage
Checking Damage
Checking Damage
When completing body and frame repairs, the front body and underbody dimensions must be correct, because these dimensions directly affect wheel alignment and steering angles...
Other information:
Nissan Murano (Z52) 2015-2024 Service Manual: Parking Brake System
Inspection and Adjustment INSPECTIONPedal StrokeOperate the parking brake pedal with a force of 196 N (20.0 kg-f, 44.1 lb-f). Check that the pedal stroke is within the specified number of notches. (Check it by listening to the clicks of the ratchet.) Number of notches : Refer to Parking Brake Control...
Nissan Murano (Z52) 2015-2024 Service Manual: P01f0 Engine Coolant Temperature
DTC Description DTC DETECTION LOGIC DTC CONSULT screen terms (Trouble diagnosis content) DTC detection condition P01F0 00 Coolant temperature (Coolant temperature relapsed below diagnostic monitoring temperature) Diagnosis condition After engine warmed up Nissan Murano Vehicle speed is more than 60km/h (37 MPH) and no fuel cut Signal (terminal) Engine coolant temperature sensor signal Threshold When the engine coolant temperature is lower than threshold value, after Nissan Murano vehicle is driven at 60km/h (37 MPH) or more for certain period...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Nissan Murano Owners Manual
- Nissan Murano Service Manual
- Warning lights
- High Beam Assist (if so equipped)
- Checking engine oil level
- New on site
- Most important about car
Front manual seat adjustment (if so equipped)
Your vehicle seats can be adjusted manually. For additional information about adjusting the seats, refer to the steps outlined in this section.
Forward and backward